In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized many fields of medicine, and one of the areas where its potential is developing particularly dynamically is dentistry. Modern dental imaging systems are increasingly supported by AI algorithms, which not only improve diagnostic accuracy but also streamline treatment processes, planning, and patient communication. With advanced diagnostic and analytical functions, dentists gain tools that allow them to work faster, more effectively, and with greater clinical confidence. Here we take the D50 Cone-Beam CT with DentalX™, the AI-powered SaaS platform as an example to witness how AI can transform digital dentistry.

Artificial Intelligence in Endodontic Practice
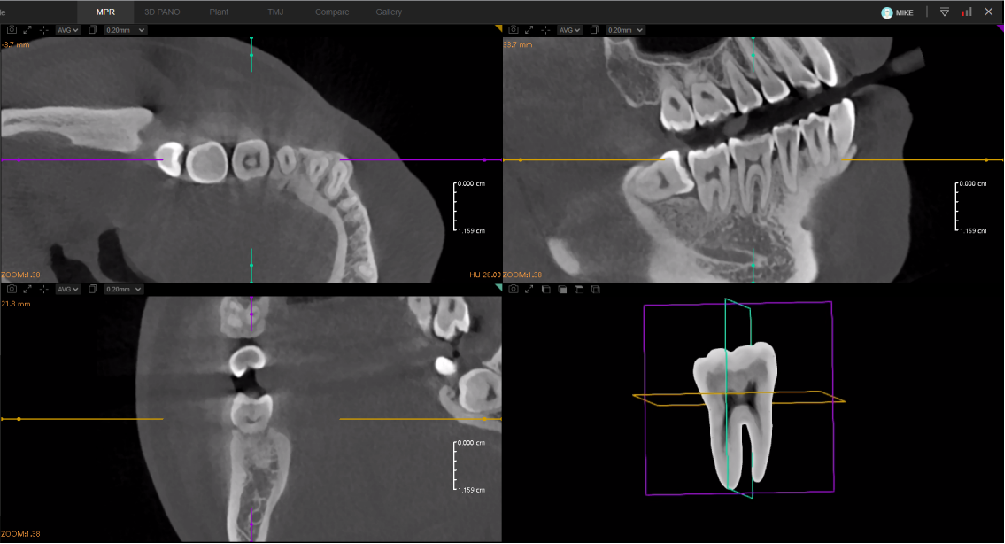
One of the most interesting applications of AI in dentistry is the three-dimensional visualization of individual teeth (Show Individual Teeth Feature is available in DentalX™), designed specifically for endodontists. Algorithms enable the generation of precise 3D tooth models from tomographic data, including root canals. Moreover, these systems offer the possibility of simulating virtual root canal fillings, allowing the dentist to plan endodontic treatment in detail before starting. This significantly reduces the risk of errors and improves the efficiency of the procedure.
Airway Analysis Using MES
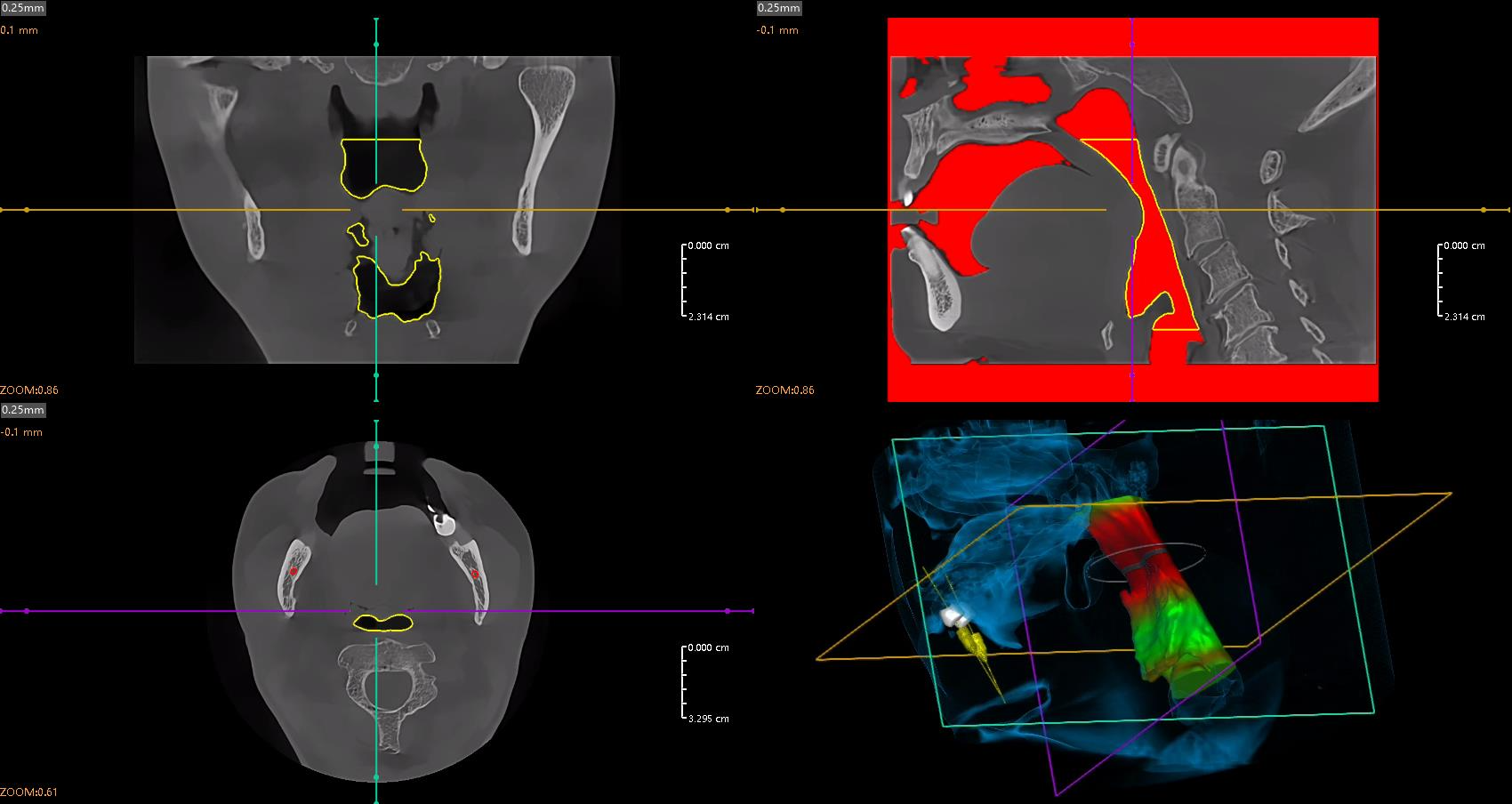
AI is also used in airway analysis, especially in the context of orthodontics and the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea. Using the Minimum Effective Section (MES) function, AI systems can automatically assess the minimal cross-section of the airways, identifying potential areas of narrowing. This type of analysis is invaluable when planning orthodontic and surgical treatments, as it allows doctors to assess how therapy may affect airway function. (Airway Analysis function is now available on DentalX™)
Intelligent Diagnostic from CBCT and Panoramic Images
Radiological diagnostics are the foundation of effective dental treatment. With the support of artificial intelligence, the analysis of images - both 3D CBCT data, 2D panoramic images, 2D Ceph images, or 2D X-Ray images - reaches a new level. AI systems can automatically identify and classify various dental pathologies, even those difficult for the human eye to detect, significantly increasing the accuracy and completeness of the diagnosis. By clicking on a detected pathology, each CT slice is automatically aligned for optimal viewing. Detected changes may include: carious lesions, impacted teeth, periapical changes, periodontal problems, and anatomical abnormalities.
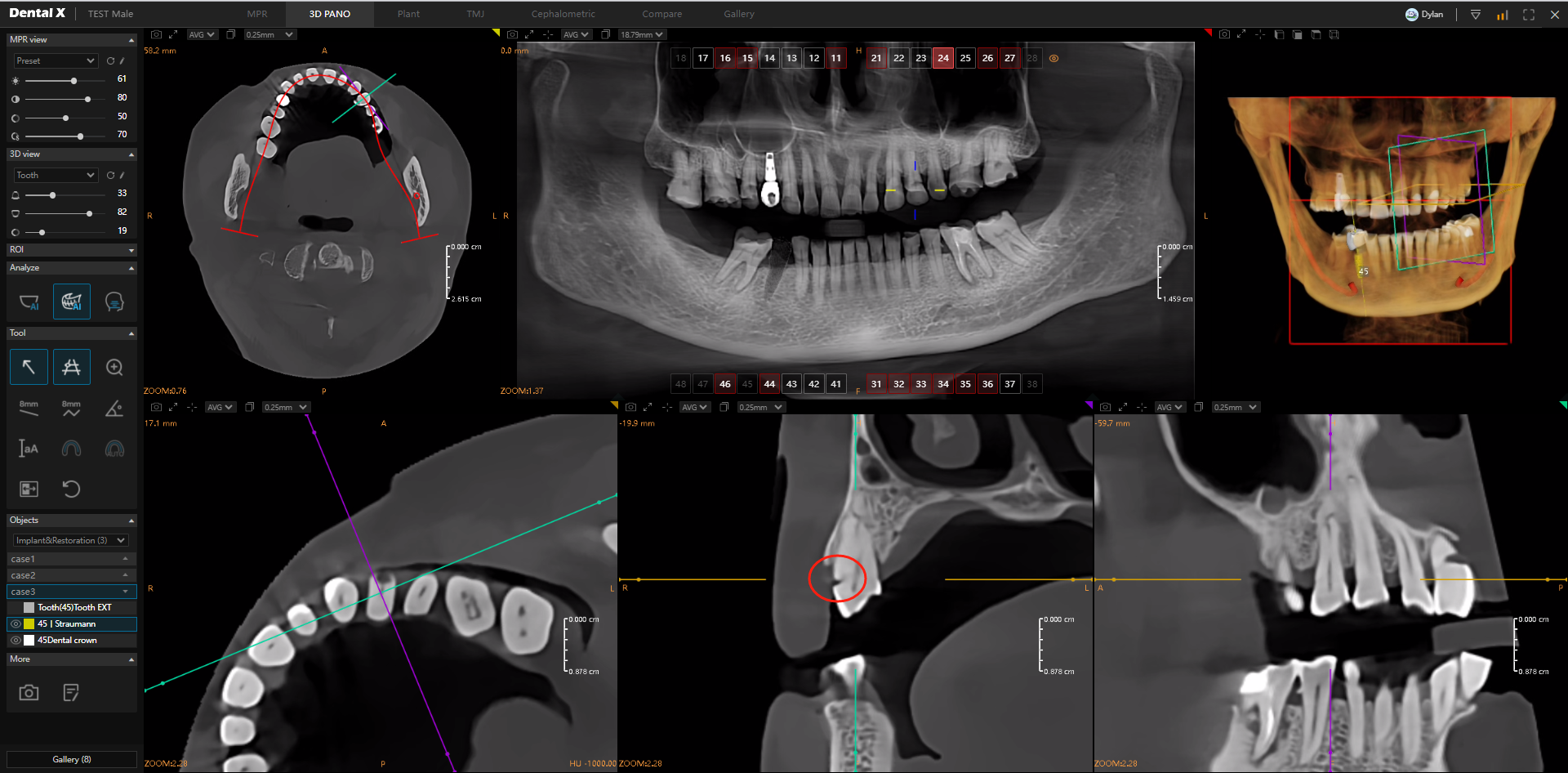
Thanks to AI, the doctor receives a comprehensive diagnostic report highlighting abnormalities on the images and offering suggestions for further steps. This reduces the risk of diagnostic error, shortens the diagnosis time, and allows the clinician to focus on treatment rather than image interpretation.
AI in Implant Planning – Precision and Safety
Implantology is one of the most demanding areas of dentistry, where precision and careful planning are critical. With artificial intelligence, the entire implant procedure planning process can be partially or fully automated, significantly increasing the predictability and safety of the procedure.
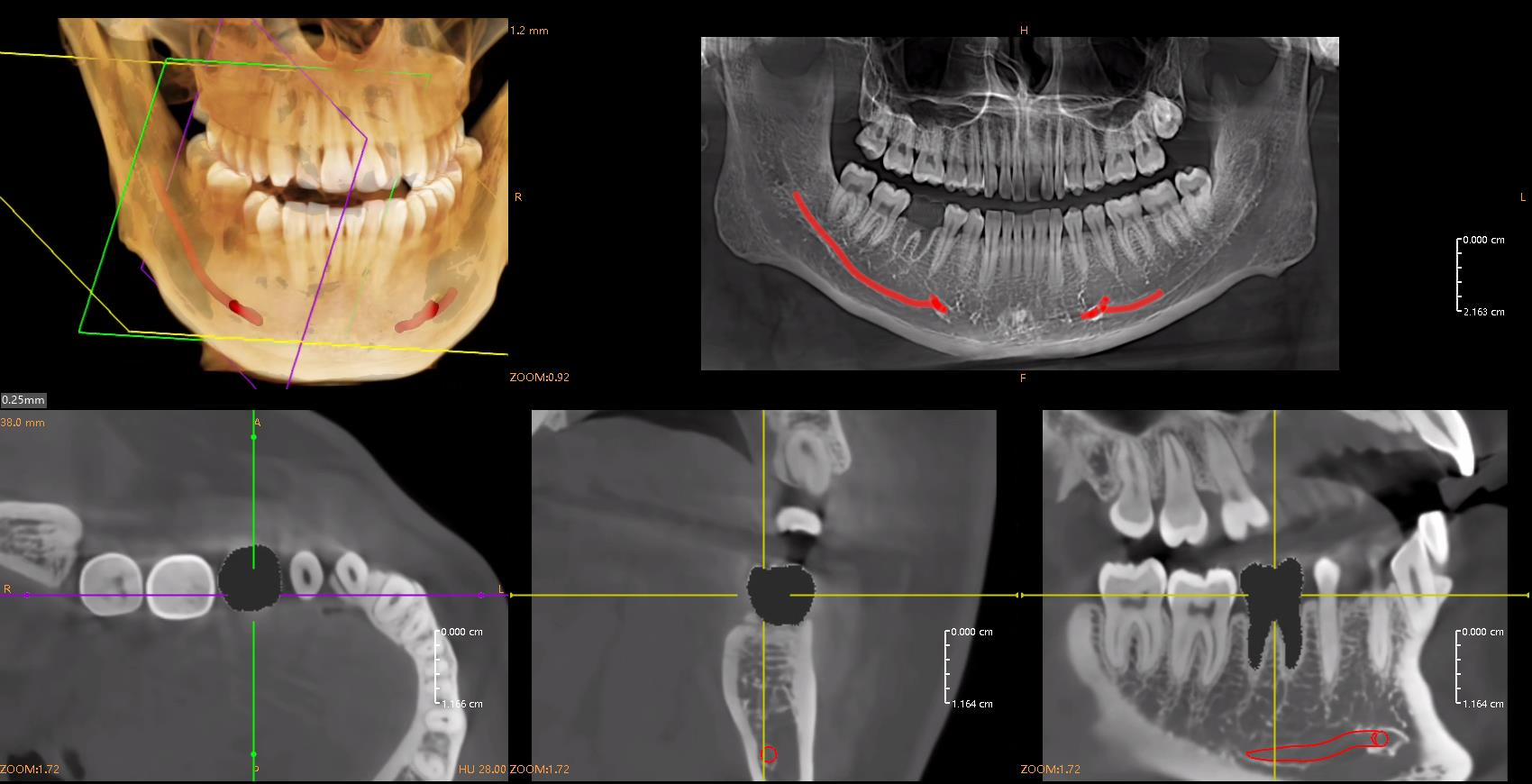
Key AI functions in implantology include:
- Virtual tooth extraction
- Automatic bone condition analysis
- Implant selection (length and diameter)
- Automatic implant positioning
- Final result simulation.
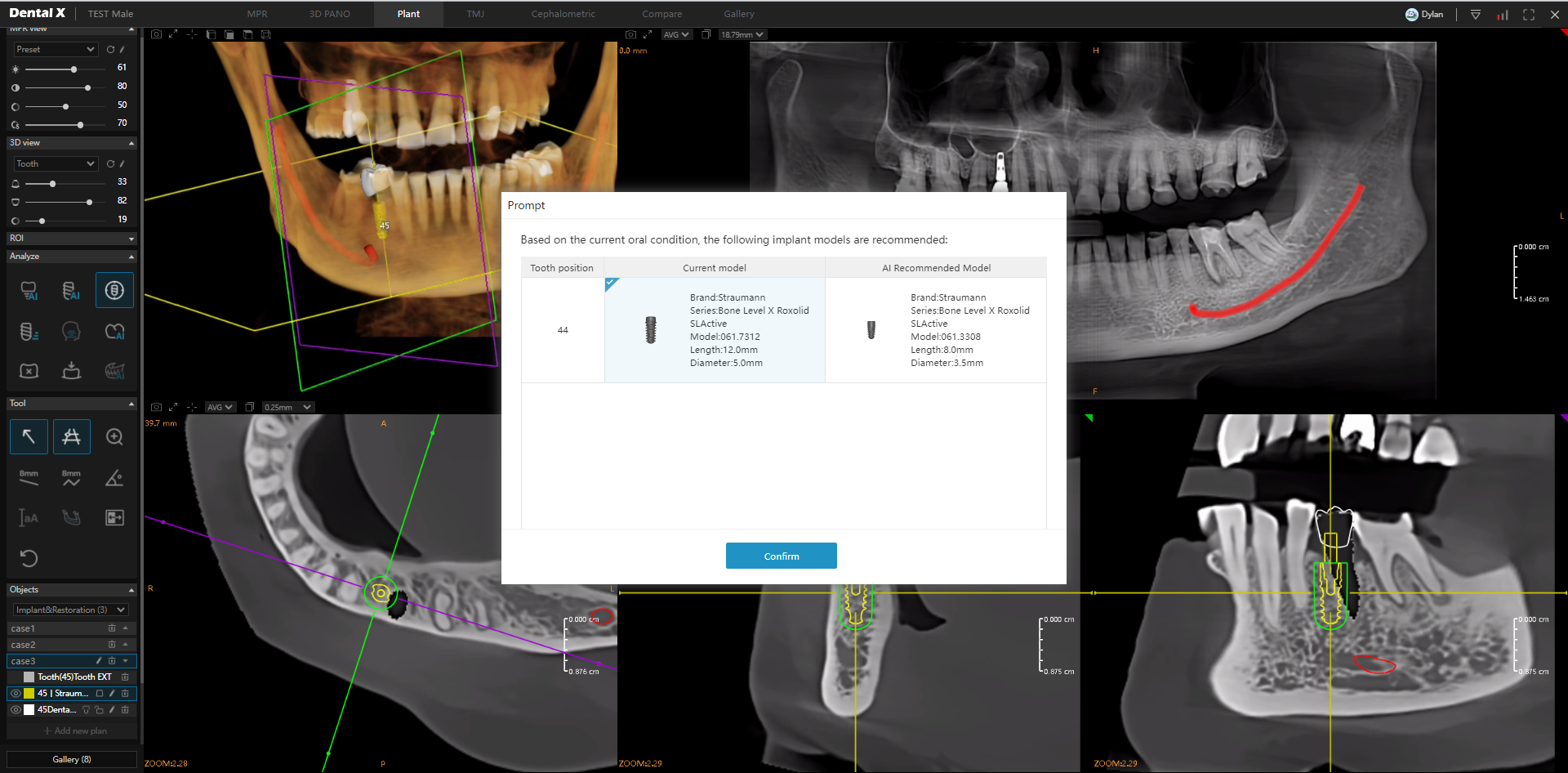
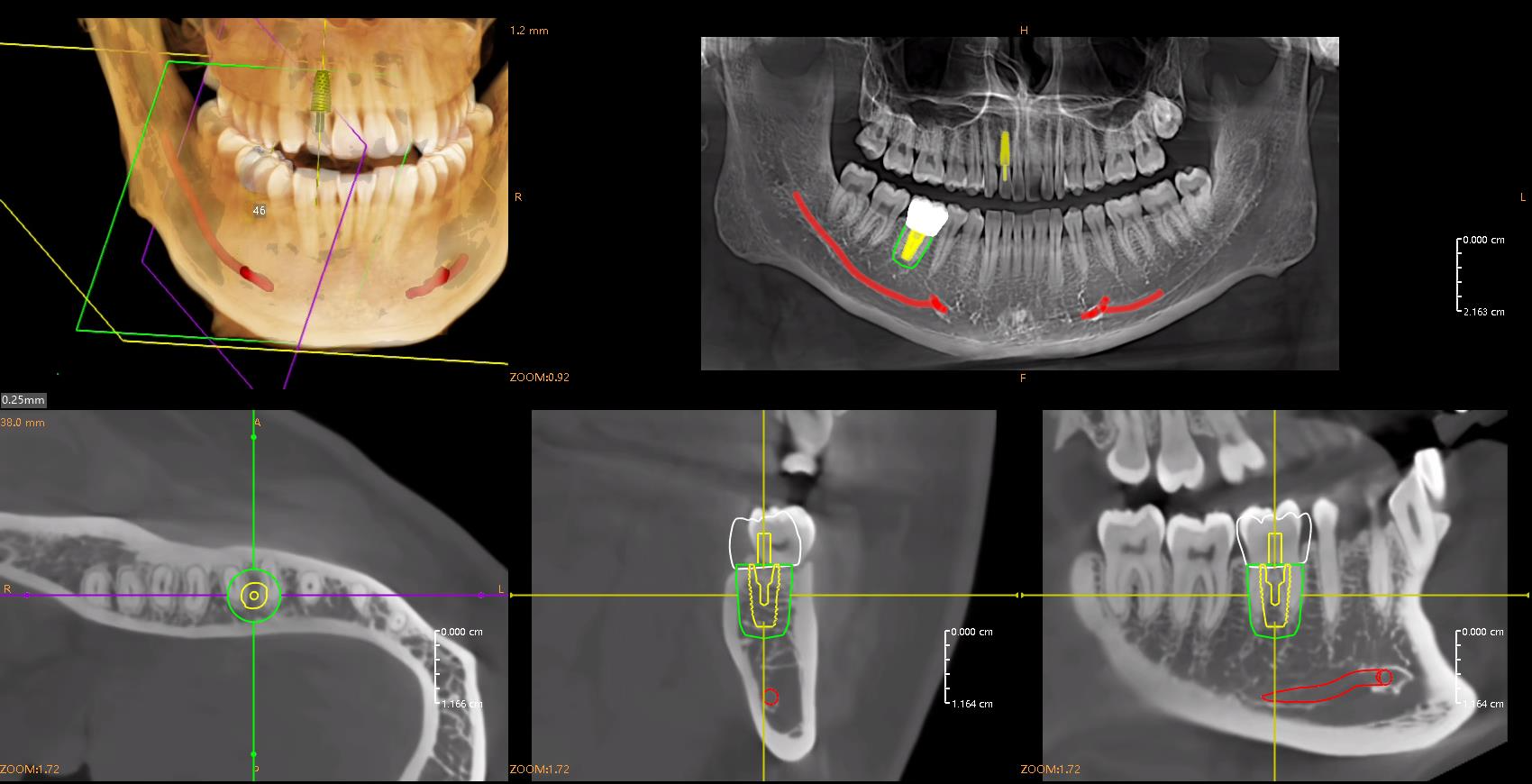
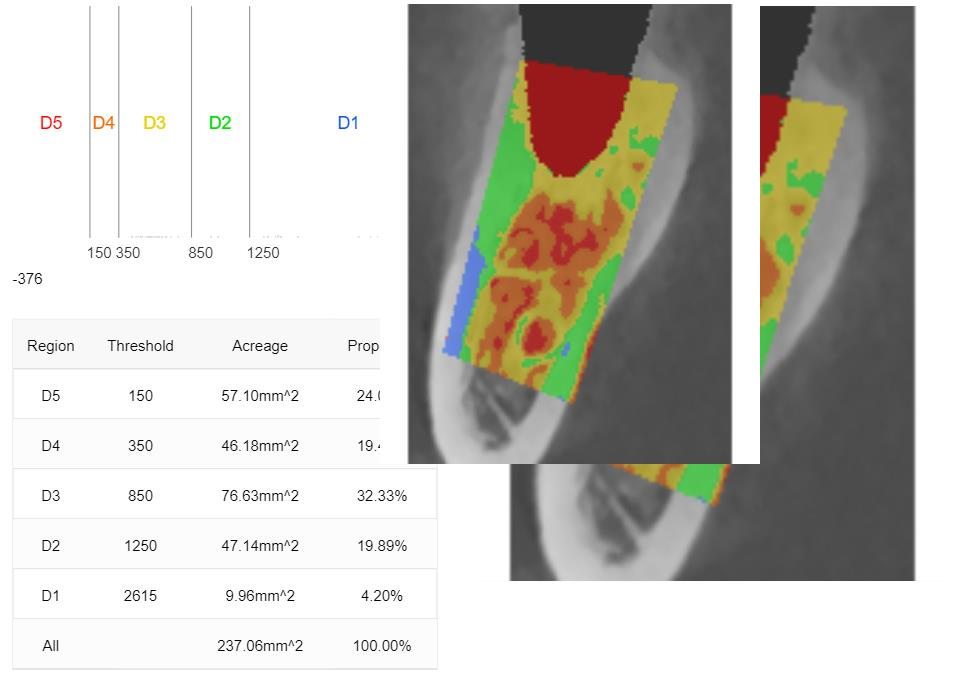
The entire process can be completed in just a few minutes, and AI solutions often exceed the accuracy of traditional manual planning. Furthermore, the data can be immediately sent to a milling machine or 3D printer to create a surgical guide, enabling minimally invasive procedures.
Automatic Cephalometric Analysis
Modern AI systems in orthodontics not only recognize anatomical landmarks on cephalometric images but also perform automatic measurements according to selected protocols. AI algorithms can calculate linear distances, angles, and skeletal-dental-soft tissue relationships within seconds, eliminating errors from manual analysis. The clinician can choose from many standard analysis methods (e.g., Steiner, McNamara, Tweed, Sassouni) and receive a complete diagnostic report that can be used immediately in treatment planning. Automation of measurements not only increases precision but also significantly reduces the time needed for analysis, allowing the orthodontist to focus on therapeutic strategy.
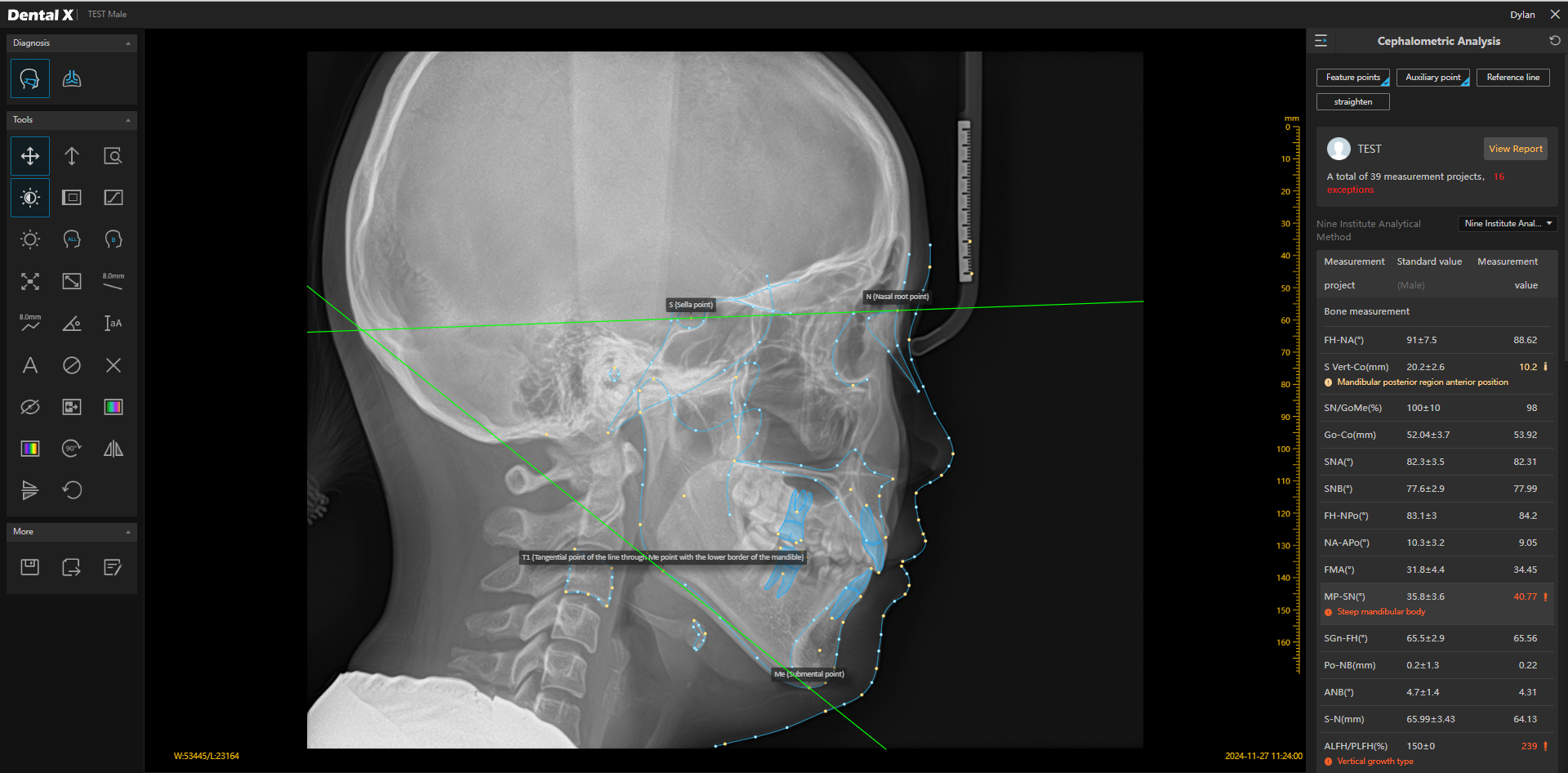
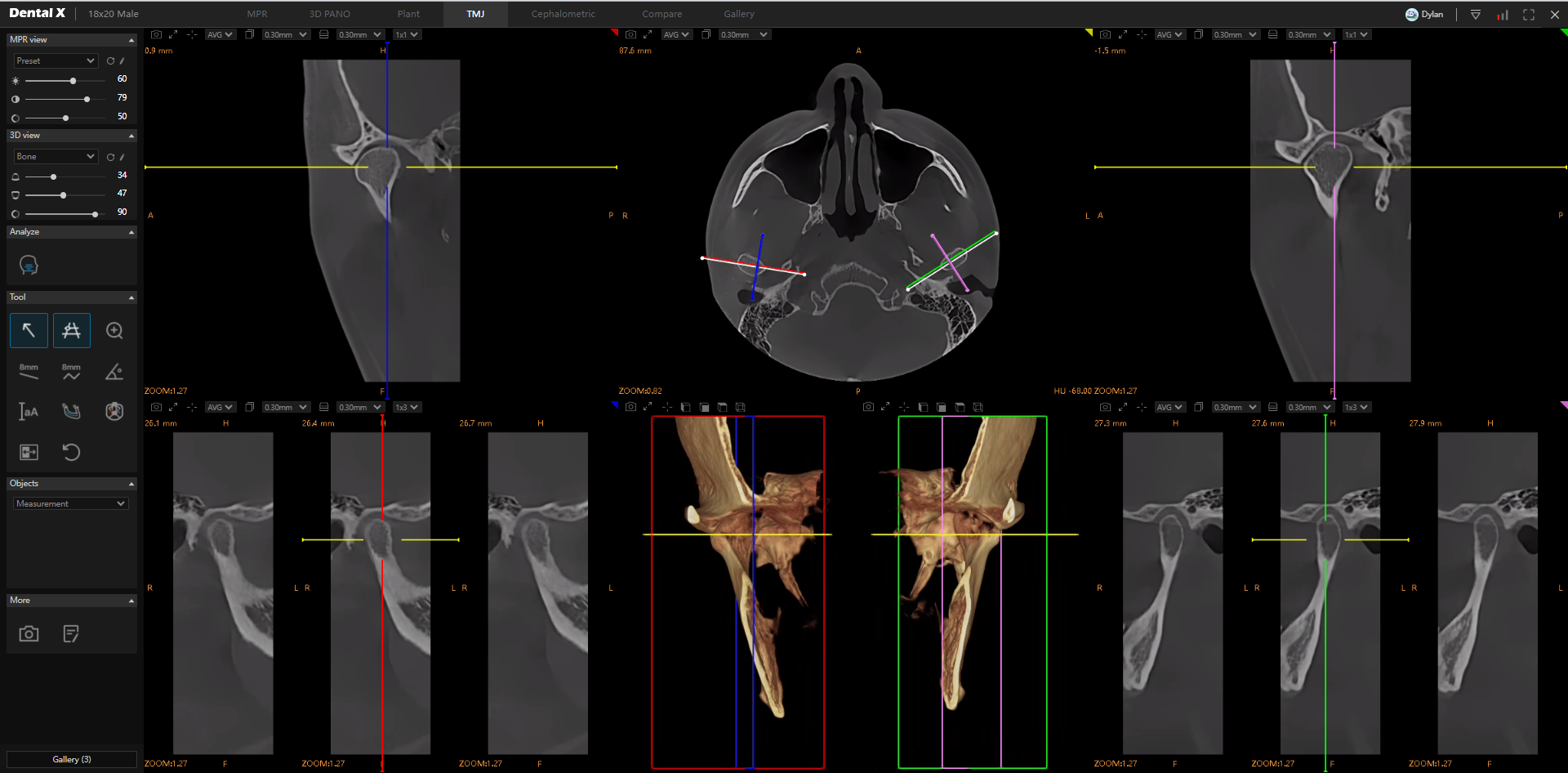
Automatic Analysis of the Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Artificial intelligence is also applied in the diagnosis of temporomandibular joints (TMJ), which play a key role in the function of the stomatognathic system. These solutions enable faster detection of functional and structural disorders that may lead to pain, joint clicking, or limited mandibular movement. Automatic TMJ analysis is a valuable tool for orthodontists, prosthodontists, and maxillofacial surgeons.
Summary
Artificial intelligence is becoming an increasingly useful and widespread tool in dentistry, although its presence is not yet standard in every dental office. Many clinics are still in the phase of implementing or testing selected AI features. Nevertheless, comprehensive solutions are already available on the market, enabling full diagnostics and treatment processes using artificial intelligence - from radiological image analysis and implant planning to the design and fabrication of customized surgical templates. The entire workflow can be automated and synchronized within a single system, significantly increasing precision, reducing treatment time, and improving the dentist’s work comfort. Such integrated solutions are currently offered only by the most technologically advanced companies but undoubtedly define the direction in which modern dentistry is heading. In the coming years, AI technologies are expected to become an inseparable part of daily clinical practice.
